Ηλεκτρονικές Υπηρεσίες
Επικαιρότητα
2025
2025
Σημαντικές Διακρίσεις
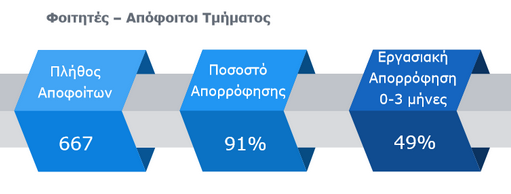
Επαγγελματική Αποκατάσταση Αποφοίτων Τμήματος
Έρευνα επαγγελματικής αποκατάστασης Αποφοίτων (2019)
Ζω στη Σάμο
Σπουδάζω στη Σάμο, σπουδάζω στο Τμήμα Μηχανικών Πληροφοριακών και Επικοινωνιακών Συστημάτων του Πανεπιστημίου Αιγαίου.
Περισσότερα ...
Τοποθεσία
Είσαι Πρωτοετής;
Συμβουλευτικός Σταθμός Σάμου
| Που στεγάζεται | Οι συνεδρίες γίνονται πλέον διαδικτυακά. |
|---|---|
| Ψυχολόγος | Δέσποινα Τσουβαλά | Επικοινωνία | E-mail: symvouleutikos-stathmos-samou@aegean.gr |
Ηλεκτρονικές Υπηρεσίες
Επαγγελματική Αποκατάσταση Αποφοίτων Τμήματος
Έρευνα επαγγελματικής αποκατάστασης Αποφοίτων (2019)
Ζω στη Σάμο
Σπουδάζω στη Σάμο, σπουδάζω στο Τμήμα Μηχανικών Πληροφοριακών και Επικοινωνιακών Συστημάτων του Πανεπιστημίου Αιγαίου.
Περισσότερα ...
Τοποθεσία
Είσαι Πρωτοετής;
Συμβουλευτικός Σταθμός Σάμου
| Που στεγάζεται | Οι συνεδρίες γίνονται πλέον διαδικτυακά. |
|---|---|
| Ψυχολόγος | Δέσποινα Τσουβαλά | Επικοινωνία | E-mail: symvouleutikos-stathmos-samou@aegean.gr |